In the quest for robust joint health, the name “collagen” often surfaces in discussions about wellness. This vital protein serves as the body’s structural backbone, playing a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of our joints, cartilage, and connective tissues. As we age, the body’s natural collagen production dwindles, prompting manny to seek supplementation to combat stiffness, discomfort, and reduced mobility. However, not all collagen is created equal. Enter the specific types of collagen: Type II,renowned for its targeted benefits in joint support,and Types I and III,celebrated for their roles in skin,bone,and muscle health. In this article, we will explore the unique properties and advantages of these collagen types, helping you make an informed decision on which may best suit your needs for optimal joint health.
Exploring the Unique Properties of Collagen Types II,I,and III for Joint Support
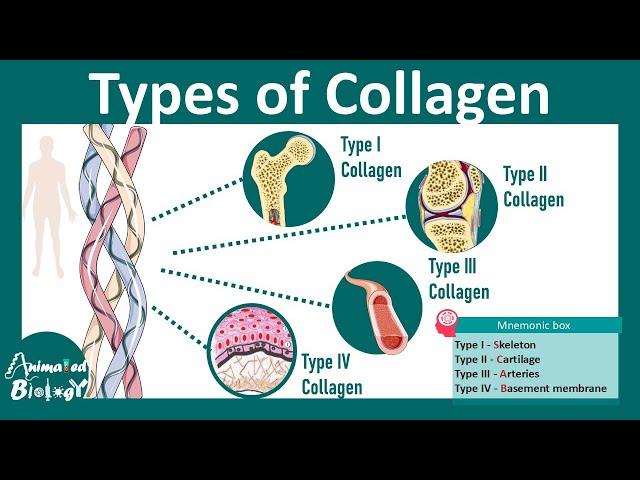
When it comes to joint support,understanding the distinct roles of collagen types can unlock their potential benefits. Type II collagen, primarily found in cartilage, serves as a crucial component for maintaining the structure and integrity of joint tissues. It provides essential support for cushioning and is naturally present in the cartilage that absorbs impact during physical activity. For those dealing with joint discomfort or conditions like osteoarthritis,supplementation with Type II collagen may help enhance joint mobility and reduce overall inflammation.
In contrast, Types I and III collagen are primarily associated with skin, tendons, and bones, but they also have significant roles in joint health. These collagen types contribute to the strength and elasticity of tendons surrounding joints, helping to stabilize them during movement. Additionally, they promote tissue repair and regeneration, which can be especially beneficial during recovery from injuries. The synergy between Types I, II, and III creates a complete support system for the joints, which is why many experts recommend a balanced approach to collagen supplementation. here’s a brief overview of their unique properties:
| Collagen Type | Primary Locations | main Benefits for Joint Health |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Skin, Tendons, Bones | Increases strength and elasticity of surrounding tissues |
| Type II | Cartilage | Supports cartilage structure and joint cushioning |
| Type III | Skin, Blood Vessels | Enhances tissue repair and overall joint stability |

Understanding the Role of Type II Collagen in Cartilage Health and Joint Comfort
Type II collagen is the main building block of cartilage, providing structural support and resilience to joints. This specialized protein strand plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and function of cartilage, which acts as a cushion between bones. As individuals age or engage in high-impact activities, the wear and tear on cartilage can lead to discomfort and decreased mobility. Including sources rich in Type II collagen in your diet or supplements can reinforce cartilage structure, possibly alleviating joint pain and stiffness.
The functionality of Type II collagen is supported by its unique composition. Unlike Type I and Type III collagen, which are primarily found in skin and connective tissues, Type II collagen has a higher concentration of specific amino acids conducive to cartilage health. Key benefits of Type II collagen include:
- Enhanced Joint Flexibility: Promotes smoother movement by providing elasticity.
- Reduced Inflammation: May help in decreasing swelling associated with joint issues.
- Promotion of New Cartilage Formation: Supports regeneration by stimulating cartilage cells.
Given these attributes, incorporating Type II collagen into your health regimen can be especially beneficial for those suffering from joint-related discomfort. Understanding its role in maintaining cartilage health is essential for anyone seeking to improve overall joint comfort.

The Synergistic Benefits of Types I and III Collagen for Overall Joint Resilience
Types I and III collagen play an indispensable role in fostering joint resilience by providing a balanced framework of support and flexibility within connective tissues. Type I collagen, known for its tensile strength, is abundant in tendons, ligaments, and within the structure of cartilage. This ensures that joints remain stable and can withstand considerable mechanical stress. Conversely, Type III collagen complements Type I by enhancing the elasticity of the tissues, making them more adaptable to dynamic movements and reducing the risk of injuries during active pursuits. Together, these collagen types create a harmonious synergy that supports not only joint integrity but also overall mobility.
Incorporating both types of collagen into a joint health regimen offers a multitude of benefits, including:
- Improved joint flexibility: Aiding in the maintenance of a full range of motion.
- Enhanced repair processes: Supporting the healing of damaged cartilage and surrounding tissues.
- Increased strength: Fortifying the structural framework of joints against wear and tear.
The combined effects of Type I and III collagen can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing joint pain or stiffness. By replenishing these essential proteins, one can promote a more resilient joint environment that caters to both stability and flexibility, contributing to improved overall joint health.

Choosing the Right Collagen Supplement: Tailoring Your Approach for Optimal Joint Wellness
When selecting a collagen supplement for joint wellness,it’s crucial to recognize the distinct benefits of various types. Type II collagen is primarily found in cartilage, making it a fantastic choice for individuals focused on improving joint function and reducing discomfort. If your goal is specifically to support joint health, look for supplements that emphasize this type, as they often contain additional ingredients like glucosamine and chondroitin which work synergistically for even greater results. You can identify these products by checking their labels for key terms such as “cartilage support” or “joint health” to ensure you are making a well-informed choice.
conversely, types I and III collagen, although not as directly linked to joint health, play a vital role in overall bodily maintenance, including the skin, bones, and tendons. If you’re seeking a holistic approach to wellness, a supplement containing both Types I and III may provide multiple benefits, including enhanced skin elasticity and stronger bones. Some collagen products mix these types, allowing for a more comprehensive support system. To simplify your decision,consider the following factors:
- Source: Marine,bovine,or chicken collagen.
- Form: Powder, capsules, or liquid.
- Additives: look for added vitamins or minerals.
| Collagen Type | Primary benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Skin, bones, tendons | Overall health |
| Type II | Joint health | Joint support |
| Type III | Skin elasticity, vascular health | Skin care |
Concluding Remarks
understanding the differences between collagen types can empower you to make informed choices for your joint health. Type II collagen stands out as the premier candidate for supporting cartilage and maintaining joint integrity, making it a top choice for those looking to alleviate discomfort or enhance mobility. On the other hand, Types I and III, which play a pivotal role in skin, tendon, and bone structure, contribute to overall resilience and well-being.
Ultimately, the best collagen for you hinges on your individual health goals and lifestyle needs. Whether you opt for Type II to target specific joint issues or incorporate Types I and III for a broader approach to wellness, integrating high-quality collagen supplementation into your routine could pave the way for healthier joints and a more active life. as you embark on your journey to bolster joint health, be sure to consult with a healthcare professional to tailor your choices to your unique needs. Here’s to robust joints and a future filled with movement and vitality!